Do you interested to find 'find the local maximum value using the first and second derivative test'? Here you can find questions and answers about the issue.
Table of contents
- Find the local maximum value using the first and second derivative test in 2021
- Second derivative test steps
- Second derivative test for local extrema calculator
- When does the second derivative test fail
- Second derivative test proof
- Second derivative test = 0
- Second derivative test example
- Second derivative test calculator
Find the local maximum value using the first and second derivative test in 2021
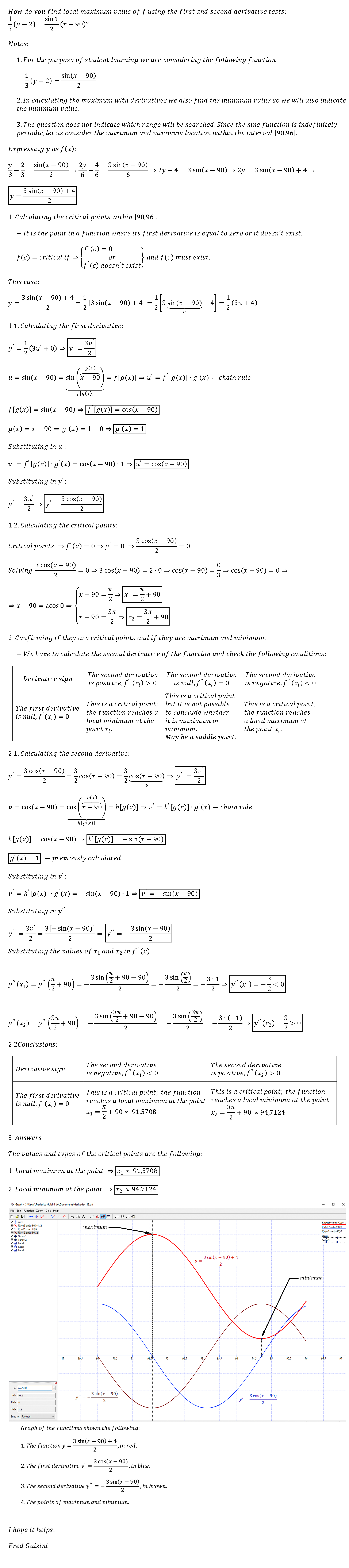 This image representes find the local maximum value using the first and second derivative test.
This image representes find the local maximum value using the first and second derivative test.
Second derivative test steps
 This image representes Second derivative test steps.
This image representes Second derivative test steps.
Second derivative test for local extrema calculator
 This picture representes Second derivative test for local extrema calculator.
This picture representes Second derivative test for local extrema calculator.
When does the second derivative test fail
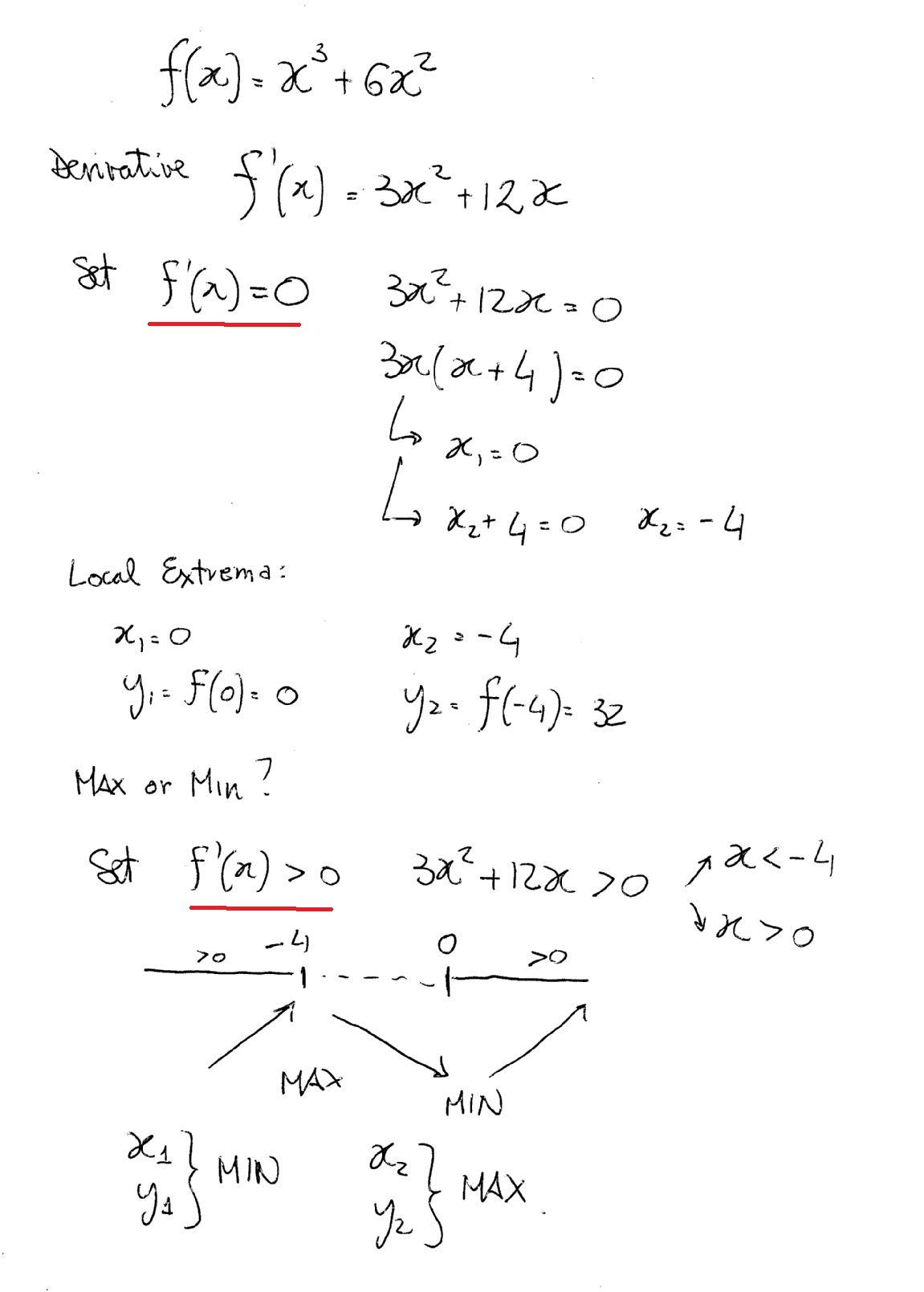 This image representes When does the second derivative test fail.
This image representes When does the second derivative test fail.
Second derivative test proof
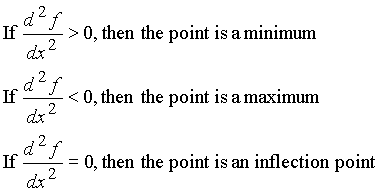 This image shows Second derivative test proof.
This image shows Second derivative test proof.
Second derivative test = 0
 This image illustrates Second derivative test = 0.
This image illustrates Second derivative test = 0.
Second derivative test example
 This image representes Second derivative test example.
This image representes Second derivative test example.
Second derivative test calculator
 This picture illustrates Second derivative test calculator.
This picture illustrates Second derivative test calculator.
How is the first derivative test used to determine maxima?
Given a differentiable function, the first derivative test can be applied to determine any local maxima or minima of the given function through the steps given below. Step 1: Differentiate the given function. Step 2: Set the derivative equivalent to 0 and solve the equation to determine any critical points.
How to find the local maximum and minimum values of f ( x )?
How do you find the local maximum and minimum values of f (x) = x x2 + 81 using both the First and Second Derivative Tests? Let's plug in f ' a value , x1 ∈ ( −9,9) . For example, for x1 = 0 Let's plug in f ' a value which is > 9 . For example, for x2 = 10
When is the second derivative of a function a local maximum?
Second Derivative Test. When a function's slope is zero at x, and the second derivative at x is: less than 0, it is a local maximum. greater than 0, it is a local minimum.
When does the first derivative test hold true?
If you could find out where the function is increasing and decreasing, we can tell whether the given critical point is a local maximum or minimum. But wait, there is a catch. This first derivative test definition holds true only if the function is continuous at the point x = a, where the test is being applied.
Last Update: Oct 2021